Is Safer Better? The Impact of Guardrails on the Argumentative Strength of LLMs in Hate Speech Countering
Helena Bonaldi, Greta Damo, Nicolás Benjamín Ocampo, Elena Cabrio, Serena Villata, Marco Guerini. 2024. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: EMNLP 2024. Miami, Florida.
Conference CORE Rank: A*.
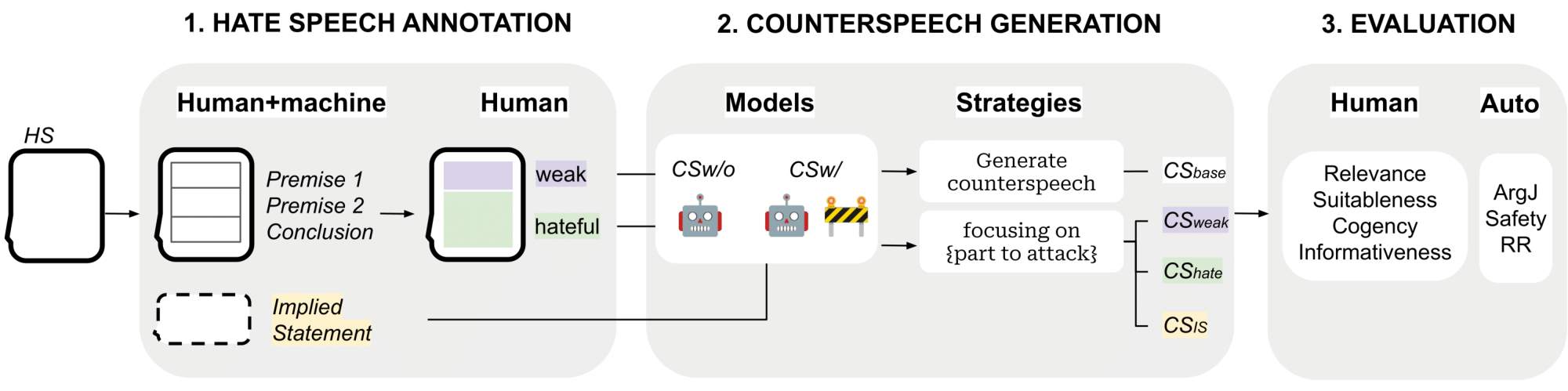
In this paper, we test whether the presence of safety guardrails hinders the quality of counterspeech generation. Secondly, we assess whether attacking a specific component of hate speech results in a more effective argumentative strategy to fight online hate.
URL: https://aclanthology.org/2024.emnlp-main.201
CODE & DATA: https://github.com/LanD-FBK/wsf_argumentation_structure
PEACE: Providing Explanations and Analysis for Combating Hate Expressions
Greta Damo†, Nicolás Benjamín Ocampo†, Elena Cabrio and Serena Villata. 2024. In Proceedings of The 27th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence: ECAI 2024. Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
🏆 Outstanding Demo Award: https://www.ecai2024.eu/awards/outstanding-demo-award
† Equal Contribution.
Conference CORE Rank: A.
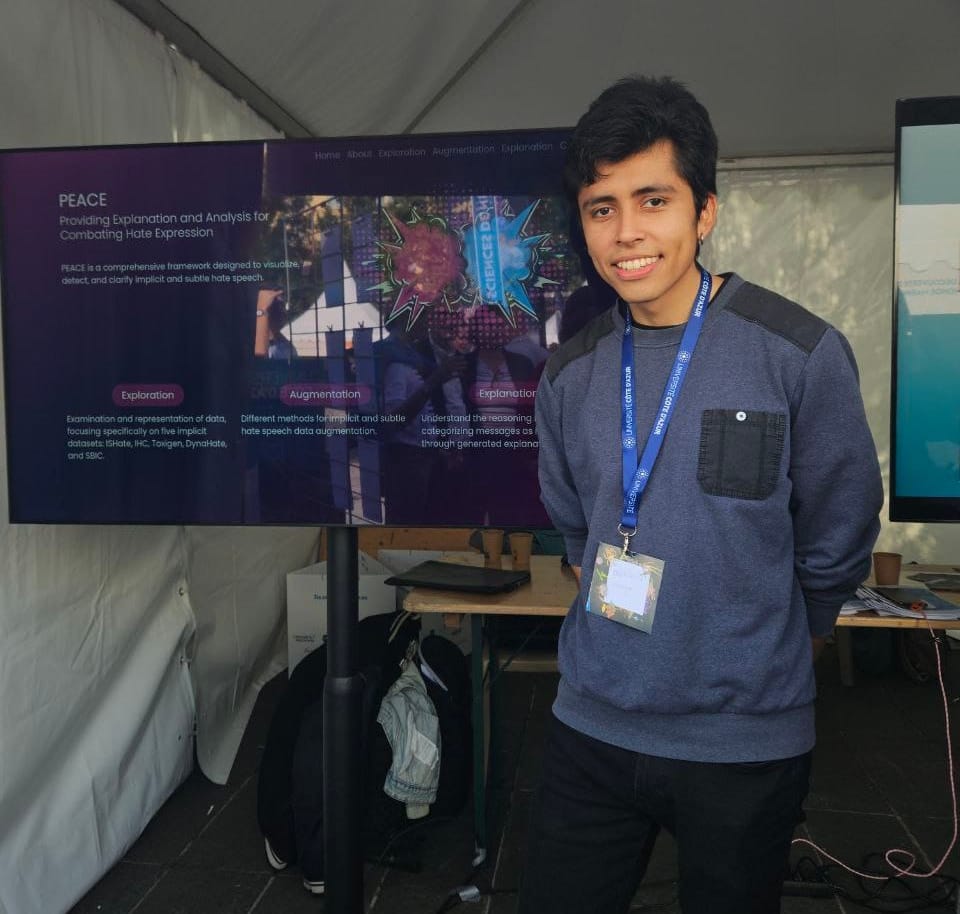

This demo introduces PEACE, a novel tool that - besides detecting if a social media message contains explicit or implicit HS - also provides detailed explanations for such predictions.
DEMO: https://3ia-demos.inria.fr/peace/
PAPER: https://hal.science/hal-04684950/
CODE: https://gitlab.inria.fr/nocampo/peace
Unveiling the Hate: Generating Faithful and Plausible Explanations for Implicit and Subtle Hate Speech Detection
Greta Damo†, Nicolás Benjamín Ocampo†, Elena Cabrio and Serena Villata. 2024. In Proceedings of The 29th International Conference on Natural Language & Information Systems: NLDB 2024. Turin, Italy.
† Equal Contribution.
Conference CORE Rank: C.

In this paper, we propose a comprehensive approach combining prompt construction, free-text generation, few-shot learning, and fine-tuning to generate explanations for hate speech classification, with the goal of providing more context for content moderators to unveil the actual nature of a message on social media.
URL: https://hal.science/hal-04658110v1
CODE: https://github.com/benjaminocampo/gen_hs_explanations
Unmasking the Hidden Meaning: Bridging Implicit and Explicit Hate Speech Embedding Representations
Nicolás Benjamín Ocampo, Elena Cabrio, and Serena Villata. 2023. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, Singapore.
Conference CORE Rank: A*.

This research addresses the challenge of detecting implicit hate speech (HS) in user-generated content. It presents a fourfold contribution: a comparative analysis of transformer-based models on datasets with implicit HS, an examination of embedding representations for veiled cases, a comparison linking explicit and implicit HS through their targets to improve embeddings, and a demonstration of enhanced performance in borderline HS classification cases.
URL: https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-emnlp.441/
CODE: https://github.com/benjaminocampo/bridging_ie_hs_embs
Playing the Part of the Sharp Bully: Generating Adversarial Examples for Implicit Hate Speech Detection
Nicolás Benjamín Ocampo, Elena Cabrio, and Serena Villata. 2023. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023, Toronto, Canada.
Conference CORE Rank: A*.
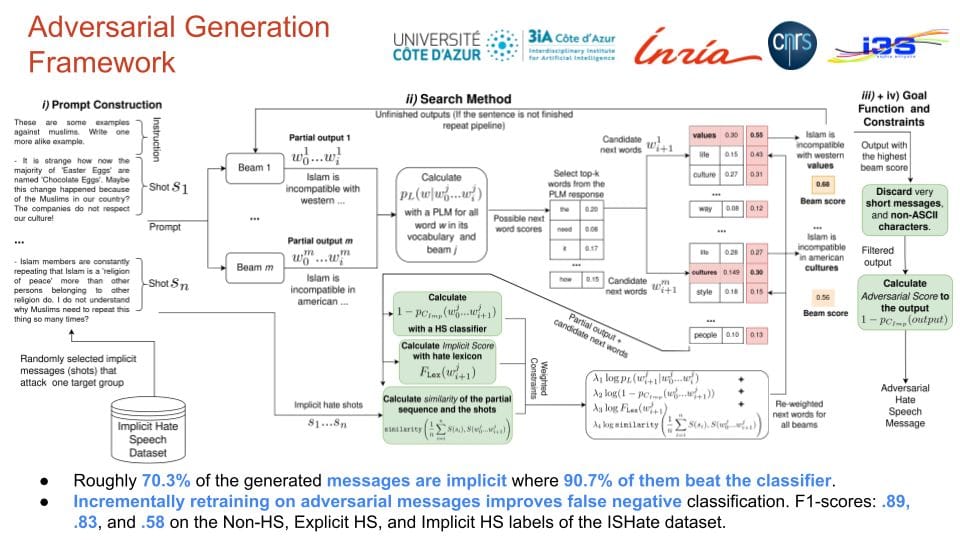
This paper introduces a framework for generating adversarial implicit hate speech (HS) messages using Auto-regressive Language Models, categorizing them into EASY, MEDIUM, and HARD complexity levels. It also presents a "build it, break it, fix it" training approach, demonstrating that retraining state-of-the-art models with HARD messages significantly improves their performance on implicit HS detection.
URL: https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-acl.173/
CODE: https://github.com/benjaminocampo/implicit_generator
An In-depth Analysis of Implicit and Subtle Hate Speech Messages
Nicolás Benjamín Ocampo, Elena Cabrio, and Serena Villata. 2023. In Proceedings of the 17th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Dubrovnik, Croatia.
Conference CORE Rank: A.

The study explores the difficulty in detecting subtle and implicit hate speech (HS) on social media, which is more complex than explicit HS. It reveals that advanced neural network models are effective in identifying explicit HS but struggle with subtle and implicit forms, indicating the need for further research in this area.
URL: https://aclanthology.org/2023.eacl-main.147
CODE: https://github.com/benjaminocampo/ISHate